CTA – computed tomography angiography
Computed tomography angiography (CTA) is a major advance in medical diagnostic imaging. By providing detailed 3D images of blood vessels throughout the body, CTA has revolutionised the way doctors diagnose and plan treatment for many vascular diseases. This non-invasive method, which provides accurate and rapid results, has been embraced by both specialists and patients seeking a safe and effective diagnosis.
Angiography versus CTA – the evolution of techniques
While still useful in some cases, traditional angiography is a more invasive and risky method. CTA eliminates the need to physically insert a catheter into a blood vessel, replacing it with the intravenous administration of a contrast agent. This state-of-the-art technology can produce a series of multi-layer images, including 3D reconstructions, with unparalleled detail.
Wide application of CTA in vascular diagnostics
CTA has a very wide application. It is commonly used to diagnose the following:
- Vascular structures in the head – CTA enables the diagnosis of aneurysms, thromboses, cerebrovascular lesions and other vascular abnormalities.
- Carotid arteries – key to diagnosing stenoses and aneurysms, as well as assessing the condition of patients before and after surgery.
- Chest – essential in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism, aneurysms, venous thrombosis, thoracic outlet syndrome and other pathologies.
- Coronary arteries – extremely useful in diagnosing coronary artery disease and assessing eligibility for cardiac surgery.
- Thoracic aorta – used to assess aneurysms, aortic dissections and other vascular pathologies.
- Renal arteries and abdominal aorta – diagnosis of aneurysms, dissections, atherosclerotic stenosis and other abnormalities.
- Lower extremity arteries – identification of pathological changes such as aneurysms and dissections.
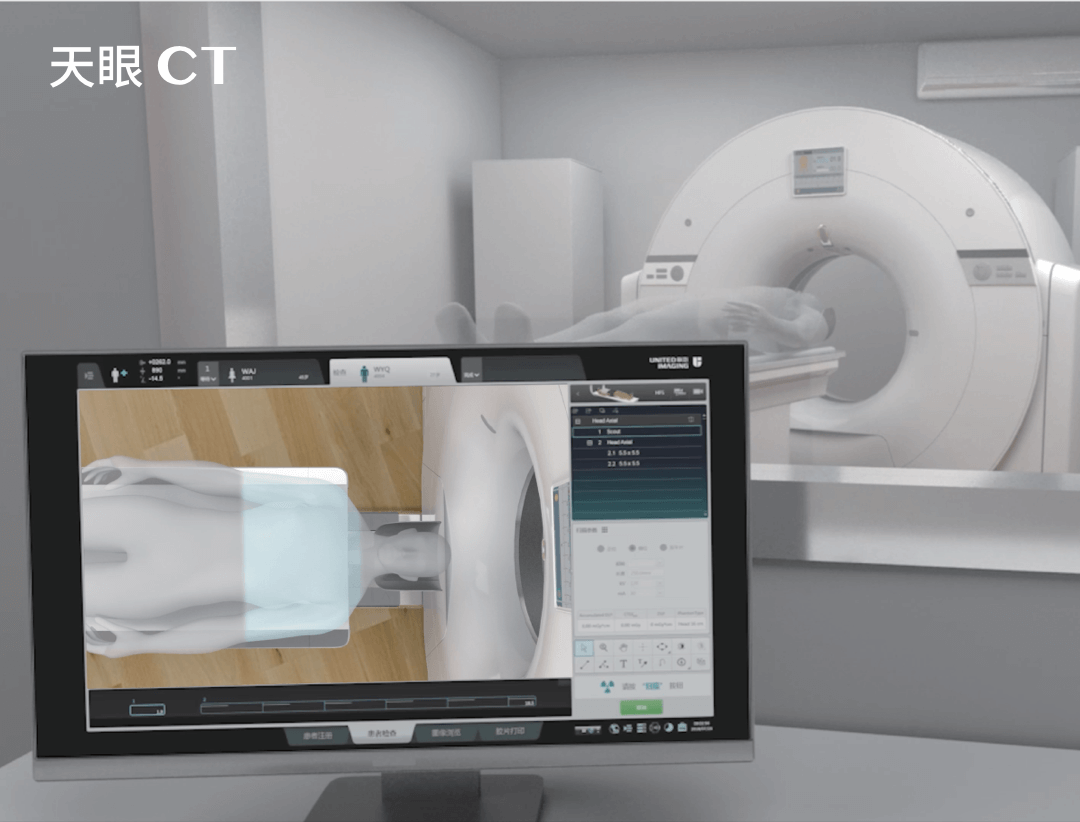
What does a CTA scan look like? Procedure and preparation
Before a CTA scan, the patient must be fasting, but must drink plenty of fluids to speed up the removal of the contrast agent from the body. The patient lies on a moving table that slides into the CT scanner. The patient must remain still for the images to be accurate. The whole procedure usually takes between 20 and 40 minutes. After the examination, it is recommended that the patient stays in the medical facility for about 30 minutes to observe his or her reaction to the administration of the contrast agent.
The contrast agent is usually given through an intravenous line (cannula). The CT scanner then takes a series of X-rays to create detailed models of the blood vessels. CTA allows blood vessels to be analysed in all possible planes, and modern CT scanners can produce images with an accuracy of less than 1 mm.
Contraindications to CTA
Although CTA is a safe and effective diagnostic tool, there are certain contraindications. These are mainly related to the need to administer contrast media and exposure to X-rays. The main contraindications to CTA are pregnancy, allergy to iodinated contrast media and renal failure. Caution should also be exercised in patients with a history of allergies, asthma or thyroid disease. The patient should also inform the doctor of any medications or medical conditions that may interfere with the procedure.
CTA – safety and effectiveness
CTA is a much safer test than traditional angiography because of its reduced invasiveness and minimised risk of complications. Importantly, the modern contrast agents used are better tolerated by the body, although there is still a risk of allergy. However, it is not recommended for pregnant women because of the radiation exposure.
At the same time, it should be mentioned that the innovative solutions incorporated in the United Imaging Healthcare systems make it possible to obtain very accurate results with low radiation doses, which significantly increases the safety of the examination.
Computed tomography angiography is a fast, accurate and safe alternative to traditional angiography. It is particularly useful for diagnosing and monitoring vascular disease, including coronary artery disease, aneurysms and thrombosis, and for assessing vascular conditions before and after surgical procedures. Its speed and minimal risk of complications make CTA an ideal choice for patients and physicians seeking advanced vascular diagnostics.
*ATTENTION! The information contained in this article is for informational purposes and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Each case should be evaluated individually by a doctor. Consult with him or her before making any health decisions.