Shoulder MRI – what is it, who is it for and how should I prepare?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder is an advanced medical imaging technique that plays an important role in diagnosing shoulder joint disorders and injuries and subsequent treatment planning. It provides detailed images of the soft tissues, tendons, muscles, bones and other shoulder structures, enabling the condition of the joint to be accurately assessed, pain sources to be located, the extent of injury to be identified and treatment progress to be monitored.
Indications for a shoulder MRI scan
One of the main indications for this examination is suspected damage to the rotator cuff tendons responsible for shoulder mobility. Overuse injuries are common in athletes, especially in shoulder-intensive sports such as swimming, tennis and throwing in athletics. A shoulder MRI scan makes it possible to assess not only the condition of the rotator cuff tendons, but also other potential sources of problems, including degenerative changes, inflammation and muscle microtrauma.
In addition, this examination is indispensable in the diagnosis of shoulder joint dislocations and instability. It makes it possible to assess damage to structures that stabilise the joint, such as ligaments, the joint capsule and glenoid labrum. Chronic shoulder pain that does not respond to standard treatment also requires more detailed diagnosis. MRI can show subtle pathologies that may be missed by other imaging modalities, such as X-ray or ultrasound, thus enabling the source of pain to be clearly identified and targeted treatment to be implemented.
Another important indication for an MRI scan is evaluating shoulder condition post-surgery. This examination provides valuable information on the healing process, possible complications, such as infections or adhesions, and also allows the quality of surgical procedures performed to be assessed, which is important for both patients and doctors monitoring the progress of treatment.
SEE ALSO: ABDOMINAL CT SCAN
Contraindications to the examination
MRI scan of the shoulder is considered a safe diagnostic method that does not expose the patient to ionising radiation. Nevertheless, there are some contraindications to this examination, such as the presence in the patient’s body of metal implants, such as pacemakers or neurostimulators, which may interfere with the magnetic field. In such cases, a detailed consultation with a doctor is necessary before the examination is performed.
Preparing for a shoulder MRI scan
Although in most cases patients are not required to adopt any special diet or make any physical preparations, it is important that the patient’s clothing be free of metallic elements that may interfere with the magnetic field generated by the MRI scanner, since this affects the quality of the images obtained. If this is not possible, many facilities offer special gowns designed for the examination.
Where a contrast agent is to be administered, creatinine levels in the blood must be tested beforehand, usually a maximum of 7 days before the scheduled MRI. This allows assessment of kidney function, which is important for the safety of the procedure. The patient may eat and drink normally and take medications before the contrast-enhanced examination, unless otherwise instructed by the doctor.
SEE ALSO: CT UROGRAPHY
Course of the examination
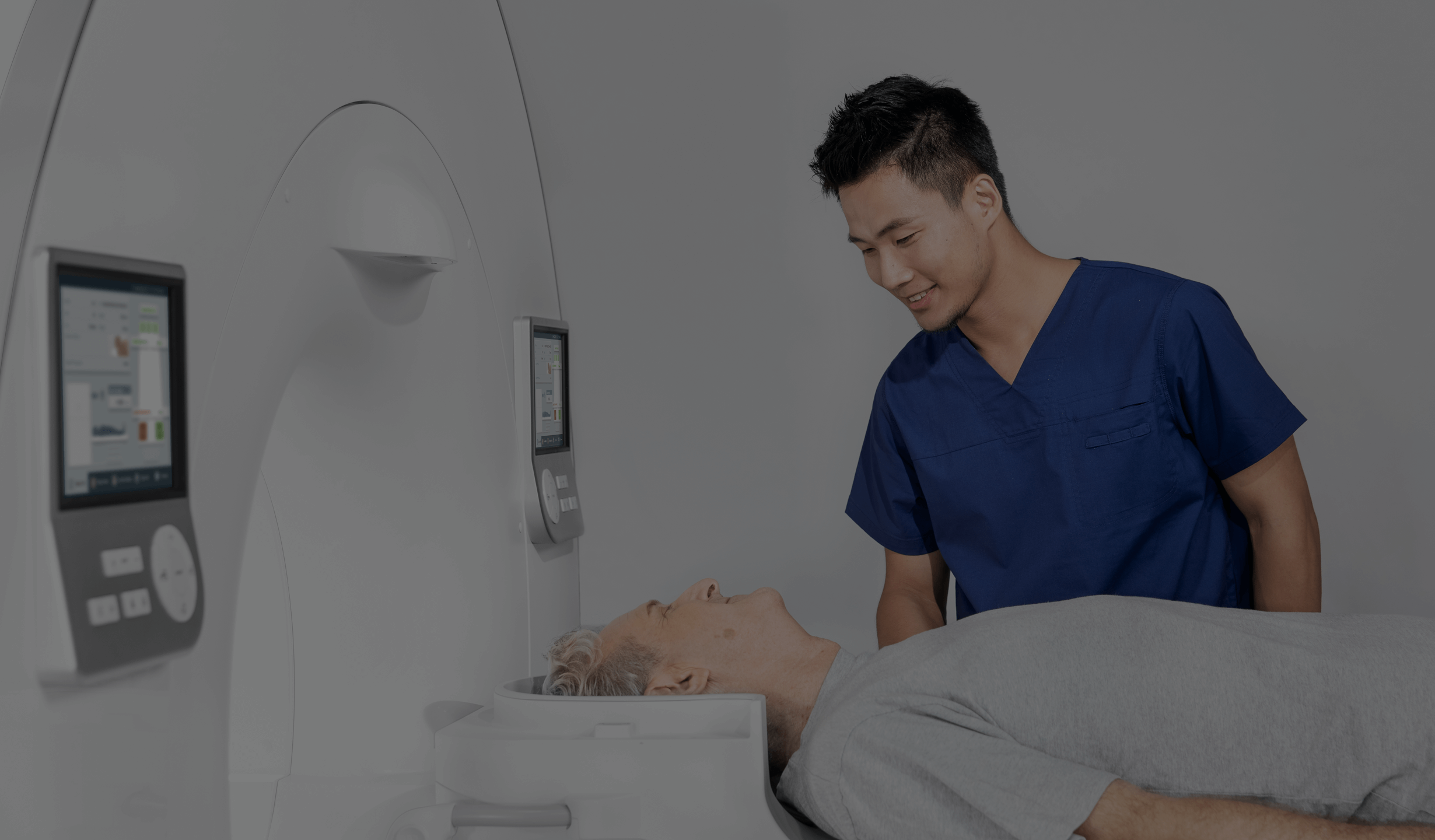
During an MRI scan, the patient lies on a moving table. The arm is placed in a specific manner to ensure optimal imaging conditions. The patient must remain motionless throughout the scan. The examination may take from 30 to 60 minutes depending on diagnostic needs and the type of imaging sequences performed.
For patients who suffer from claustrophobia, anxiety may pose an additional challenge, but many facilities offer sedatives or use more open MRI scanners to increase patient comfort.
Shoulder scan MRI results are subsequently analysed by a radiologist who prepares a detailed report. On the basis of the images obtained, it is possible to accurately assess the condition of the shoulder structures, which allows the attending physician to make a diagnosis and plan appropriate treatment. Shoulder MRI can often detect problems that cannot be identified with other diagnostic methods, such as X-ray or ultrasound, making it an invaluable tool in medical diagnosis.
It should be noted that although shoulder MRI scans are extremely helpful in diagnosis, the final interpretation of the results should always be performed in the context of the patient’s complete clinical picture, including medical history and symptoms as well as the results of other examinations. Only a comprehensive assessment will make it possible to select the most appropriate treatment.
THIS MAY ALSO INTEREST YOU: FLAIR SEQUENCE IN MRI – WHAT IS IT?
*ATTENTION! The information contained in this article is for informational purposes and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Each case should be evaluated individually by a doctor. Consult with him or her before making any health decisions.